We Are Always Here for Your Health.
A Healthy life is everyone's right!
FILL IN THE FORM TO GET QUOTE
Orthopedics and Traumatology
What is Orthopedics and Traumatology?
Orthopedics and Traumatology set the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal system disorders, the trauma injuries, the disorders of hand, shoulder, elbow and knee. Orthopedics and Traumatology, which was created principally for the treatment of congenital disabilities, has developed over time and has become a medical department that includes the treatment of many disorders and injuries.
Subdivisions of Orthopedics and Traumatology
- Arthroplasty surgery (joint prostheses)
- Sports traumatology
- Height lengthening and leg inequalities
- Pediatric orthopedics and traumatology
- Hand surgery and microsurgery
- Knee surgery and arthroscopic surgery
- Shoulder and elbow surgery
- Orthopedic oncology
- Foot and ankle surgery
- Bone inflammation treatment
Which Diseases does Orthopedics and Traumatology Deals with?
- Congenital hip dislocations
- Inequalities in the legs
- Meniscus injuries
- Contusions and sprains in the joint ligaments
- Nerve compressions
- Trigger finger
- Tennis elbow
- Joint calcifications
- Sciatica
- Plantar fasciopathy
- Cartilage injuries
- Tendon tears
- Bone fractures
- Bone inflammations
- Dislocations in different joints
- Joint pains
- Rheumatisms
- Neck and spinal disc herniations

Knee Surgery
In cases where the cartilage is abraded in the disorders such as osteoarthritis and calcification or the knee joint is damaged due to some diseases, a knee replacement is a corrective surgery that has been applied for many years. This surgery is performed by removing the damaged parts of the cartilage, with some of the bone underneath, and correcting the deflected axis of the knee joint and placing the prosthesis made of various metals into the joint.
The prosthesis consists of two metal parts and a plastic part between them, resulting in a metal joint that can mimic the movements of a normal knee joint.
In addition, when only one part of the patient's knee is impaired, there is also a partial knee prosthesis that can be applied in special cases. The picture shows the x-ray radiographs of the knee of a patient with osteoarthritis on the knee joint before the surgery and after the placement of a complete knee prosthesis.
The Patients Who Can Have a Knee Prosthesis
The limitations in daily functions, a decrease in knee movements, the difficulties in walking and climbing up and down the stairs arise due to the pain, and the pain is the basic requirement of the knee prosthesis. First of all, the main cause of the pain is investigated, and the pain and functional limitations are tried to be eliminated with non-interventional treatments. If the problem cannot be solved as a result of these procedures, a prosthesis surgery may be required.
The knee prosthesis surgery can be applied in cases of calcification of the knee joint cartilage due to an unknown cause, of intra-articular fractures that cause a cartilage abrasion, in the diseases that cause deformation of the knee joint axis due to the deformities, the diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, the bone death (osteonecrosis) and the other diseases of the knee joint that cannot be treated resulting in a chronic pain. Knee prosthesis is definitely not applied during the active infections around the knee.
The Importance of Age and Weight in Knee Replacement Operations
GA knee prosthesis is not applied to the young patients except for mandatory cases, since other methods are preferred to protect the joint and cartilage in knee disorders in young patients. In addition, the knee prostheses are used more frequently in patients over the age of 60. In the past years, when the technology was not developed yet, it was a method not preferred in young patients due to the short life of prosthesis. As a result of developments in technology, the prostheses that are compatible with the human body, durable, long-lasting and providing more mobility have been produced, and the opportunity to use these prostheses when needed has emerged beginning from the age of 50.
In deciding on the knee replacement operation to be performed at an advanced age, the patient's pain, loss of function in daily life and expectations are evaluated. However, it should be kept in mind that the additional systemic diseases (the coronary vascular diseases, heart failure, diabetes, lung and kidney diseases, etc.) that may occur at later ages increase the risks of surgery. After the decision of knee replacement operation in the patients in the aforementioned age groups, any possible additional problems are determined by performing detailed examinations (check-up). If the additional problems that arise as a result of the screening cause an increase in the risk of surgery, the pros and cons of the surgery to be performed are reviewed and a decision is made.
The rate of risk may be high due to the higher prevalence of systemic diseases such as the diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease in overweight patients. These patients whose movements in daily life are extremely restricted due to the knee problems become difficult to lose weight and generally gain more weight. As a result of the evaluation after reviewing all risks, if the risk ratio is low, the knee replacement operation will be beneficial in increasing the mobility of the overweight patients.
Risks of Knee Prosthesis
The diseases that occur during the aging may pose risks for anesthesia and surgery in the patients who are candidates for knee prosthesis. In addition, a knee replacement surgery may cause an infection (inflammation), a clot formation in the veins and mechanical problems of the prosthesis.
The risk of infection can be reduced with the well conditions of the operating room and the use of preventive antibiotics. In order to reduce the risk of infection, it is ensured that there is no infection elsewhere in the patient's body before planning the surgery. Antibiotics are given to the patients who will undergo the operation, starting before the surgery and continuing for one day after the operation. The operating room conditions are arranged in a way that eliminates the risk of infection, and the surgical team is ensured to take the necessary precautions against an infection. Despite all the precautions taken, it should be taken into account that there may be a risk of microorganisms in another part of the patient's body during and after the operation to reach to the knee joint and cause infection in the prosthesis.
A clot formation can be encountered in the veins, especially in the patients with disorders that cause a coagulation tendency and in prolonged immobility. Patients are protected from this problem by administering drugs that prevent coagulation for postoperative2-4 weeks. In addition, this problem is tried to be avoided by allowing the patient to move and walk rapidly after the surgery. Despite all the precautions taken and despite posing a small risk, the formation of clots in the leg veins and the fragments that break off the clot may cause the respiratory problems, especially by occluding the pulmonary vessels.
Nowadays, the risk of mechanical problems related to the prosthesis such as detachment, abrasion and loosening of the prosthesis is very low. In addition, the problems such as non-healing of wounds, knee movements are more limited than the expectations of the patient, a continuous pain despite a normal operation and postoperative progression are observed in an extremely low rate.
Knee Arthroscopy
In the knee arthroscopy, 2-3 holes of 0.5 cm in size are drilled into the knee joint, a small tube attached a camera at the end is transferred through the holes, and the distinctive surgical instruments are used. In this surgical treatment, the image taken from the tube attached with a camera and lens at the end is transferred to the video screen and the inside of the knee joint is screened. The tube-shaped camera, whose tip is angled and thin and called optics, is easily rotated inside the joint, allowing the structures inside the knee to be screened. The necessary surgical procedure is applied with the help of tools that are transferred through the other hole opened into the knee joint.
Is General Anesthesia Applied for a Knee Arthroscopy?
A knee arthroscopy should be performed under the operating room conditions. In this procedure, a local or general anesthesia can be applied, as well as the epidural anesthesia method, which is performed by numbing the lower body. A diagnostic arthroscopy, which can also be performed with local anesthesia, is applied in cases that require a tissue sampling from the knee, which is mostly performed before the MRI examination, but is now called biopsy. A general or epidural anesthesia is decided by considering the health problems and general condition of the patients who have problems involving the tissues such as the meniscus, cruciate ligaments or cartilage.
What Instruments Are Used For Knee Arthroscopy?
An endoscope consisting of a small tube containing the camera system, a surgical instrument called shaver, which cuts the tissues by shaving slowly and absorbs them, and a radio frequency device that cleans the tissues with radio frequency are used in the knee arthroscopy. In addition, a system called arthropump that keeps the intra-knee pressure at a certain level is used. In addition to these tools, other surgical instruments specially manufactured for arthroscopy are used in evaluating, cutting, and removing tissues.
What Are The Diseases Treated With Knee Arthroscopy?
An arthroscopic surgery method is a therapeutical treatment for the injuries of structures such as intra-articular meniscus, anterior cruciate ligament, articular cartilage, capsuil, for the septic arthritis defined as intra-articular inflammation, for the synovitis defining the inflammation and thickening of the joint membrane, for the moderate calcification of knee joint, called gonarthrosis, for the gout arthritis and intra-articular fractures.
How Long Do Patients Undergoing a Knee Arthroscopy Stay in the Hospital?
Surgery is performed in the patients who come 2-3 hours before the knee arthroscopy operation, following the preparatory procedures. Although the patients whose general condition is monitored after the operation are hospitalized approximately for one night, most of the patients are discharged on the day following the operation. Loading and standing up are determined according to the procedure applied during the operation. For instance, while the stepping on the feet is not allowed in the mosaicplasty and arthroscopic joint debridement and drilling operations, the standing on the same day is allowed after an arthroscopic meniscectomy and ligament surgeries.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction
The knee cruciate ligaments, which are the most important stabilizers of the knee joint, prevent the knee from slipping forward and backward during the activity. These ligaments can be ruptured during non-vehicle traffic accidents, and the sports such as tennis, football, skiing.
The cruciate ligaments that are ruptured for various reasons cause a severe pain in the knee, insecurity, slipping, turning, especially in the accidents that occur during doing sports. Swelling and pain occur in the knee with the rupture of the cruciate ligaments of the patients. An emergency surgery cannot be performed before the pain and swelling are healed. After the trauma, a knee ice application, bandage, knee brace and exercise treatments should be performed first. In cases with cross ligament lesions, an arthroscopic surgical treatment should be applied especially in the young, active and sportive patients. In the treatment, a new ligament should be reconstructed instead of the broken ligament.
Surgical Procedure That Should Be Done
Generally, it is not preferred to repair the broken ligament primarily, instead, a new ligament is reconstructed. Various methods are used for this purpose.
Tendon grafts such as patellar tendon, hamstring tendon, quadriceps tendon removed from the patient himself/herself
- A cadaver tendon called allograft
- Synthetic graft
- In this method, grafts removed from the patient himself/herself are preferred. During the arthroscopy surgical procedure, one of these tendons is applied to the anatomical place of the ruptured ligament. An arthroscopic repair can be successfully performed by physicians.
Movement and exercise are started immediately after the surgical procedure. In the first three weeks, the patient walks with crutches without weight. The patient starts running straight in the third month and sports activities in 4-6 months.
Intraarticular Injection Therapy
Gonarthrosis, which is applied by injecting various medications into the knee, is not usually a painful application when done properly. There is no need for local anesthesia before injection. However, the place where the needle is inserted is numbed with a cooling spray just before the injection. A feeling of fullness and tingling may be experienced in the joint within a few days after the injection. This condition, which may be the normal outcome of treatment, is temporary.
The corticosteroids (cortisone) and Hyaluronic Acids, also called "cartilage protecting agents", are injected into the knee.
Hyaluronic Acid injections are also divided into two types as "low molecular weight" and "high molecular weight". In recent years, the high molecular weight injections are commonly preferred because of their longer effectiveness and more efficient responses to the disease.
How Hyaluronic Acid Works?
Although a treatment with hyaluronic acid injection is not a powerful method that can eliminate the option of prosthesis surgery, it helps to reduce the pain caused by calcification for a certain period of time and thus can increase the patient's quality of life. In addition, it has an effect that can prolong the process leading to the surgery. In treatment with hyaluronic acid injection, the main goal is to maintain the joint lubricity and increase the durability of the cartilage by replacing the reduced hyaluronic acid in the joint.
The protective role of hyaluronic acid in the joint cartilage is also emphasized in the latest studies of the American Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Although the application is not a miraculous treatment that will eliminate the option of knee replacement surgery, it constitutes a significant step in the treatment of arthritis.
In addition to its lubricating and shock absorbing effect on the joint, Hyaluronic Acid also functions by affecting the activity of prostaglandins and cytokines that increase the inflammation in the joint.
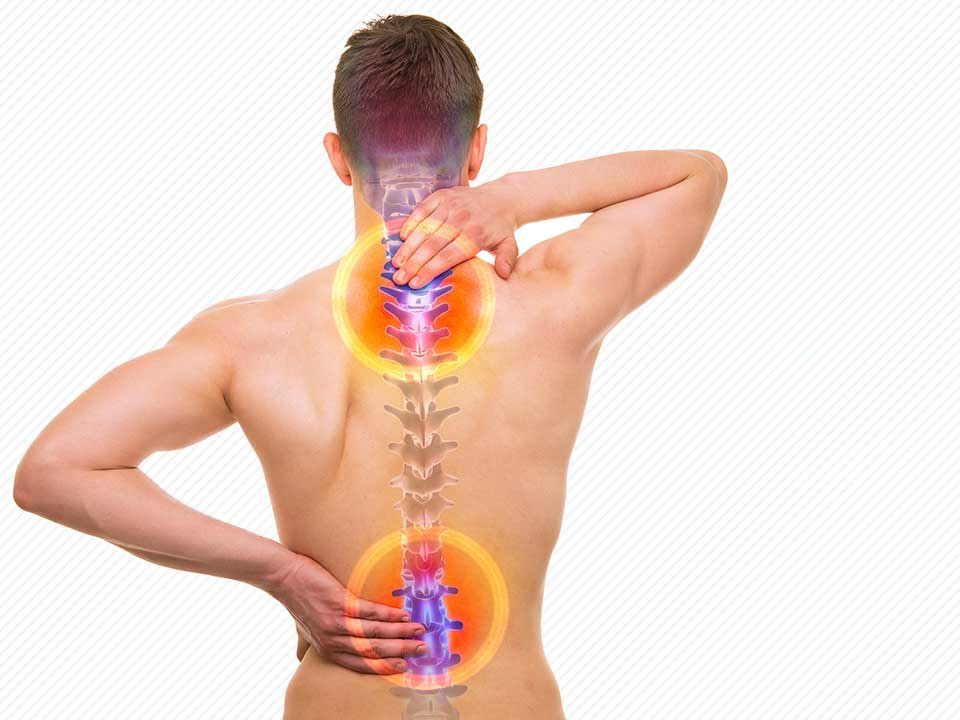
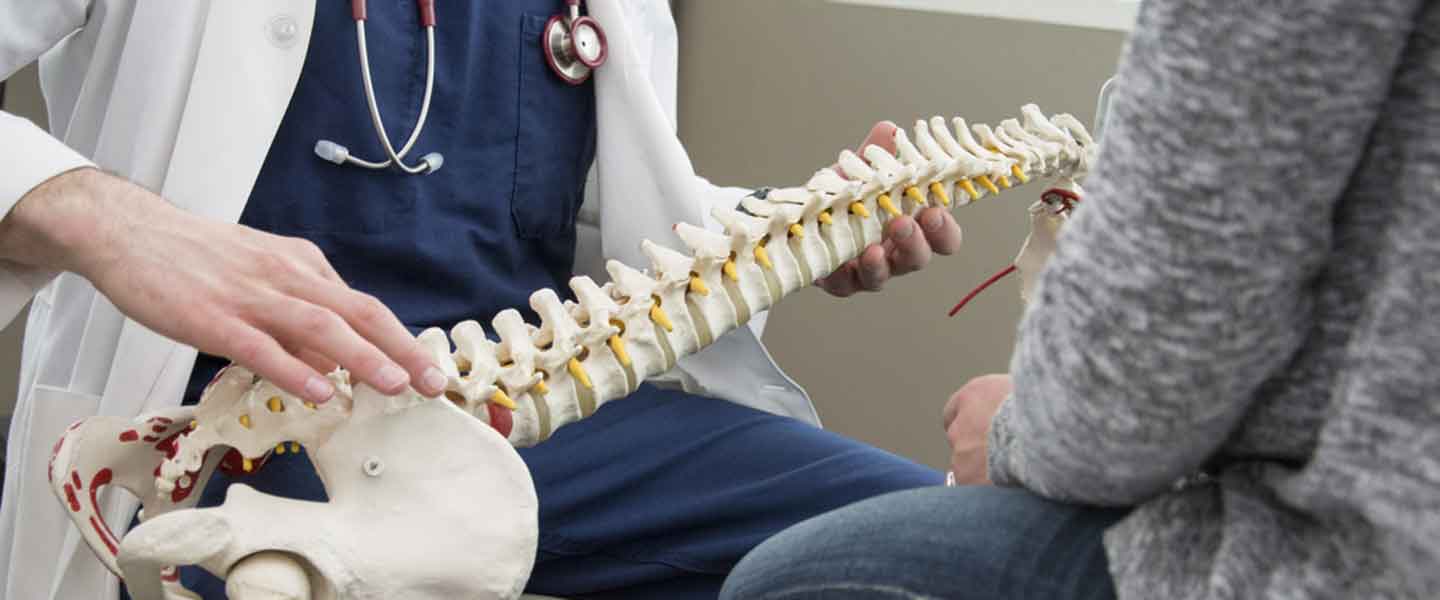
Vertebra (Spinal Surgery)
The spine defines the chain of bones that both keeps our body upright and protects the spinal cord passing through its canal. The spinal cord, also called medula spinalis, is a part of the central nervous system, which starts from the brainstem, extends to the coccyx and provides the connection between the brain and organs. All the motor (i.e., movement activities) and sensory activities of the organs are performed and controlled by the spinal cord. The spinal cord also controls the reflexes alone. Some scientific societies reveal that the pressure and irritation in the spine causes an imbalance in the connected organs, and if this state continues for a long time, several diseases emerge.
The spine consists of 33 bones, each of which are called vertebra. Although the shapes of these vertebrae differ according to the region they are located in, their general anatomical structures are the same. Vertebrae are divided into 5 groups according to these differences in shape.
Number of the Human Vertebra. 7 Cervical (Dorsal) Vertebrae. 12Thoracic Vertebrae. 5 Lumbar Vertebrae. 5 Sacral Vertebrae. 3-4 Coccygeal Vertebrae adherent to each other.
Cervical Vertebrae:
The 7 vertebrae in the neck region starting from the skull end extending to the nape of the neck are called cervical vertebrae. The motor (i.e., movement and sensory) activities of the arms and hands are controlled by the regions of the spinal cord at this level. If an injury in the spine damages the spinal cord in this area, the tenderness occurs in the arms and the lower parts of the arms (fingers).
Thoracal (Dorsal) Vertebrae:
The 12 vertebrae starting from the nape extending to the end point where the ribs merge with the spine are called thoracal vertebrae. These vertebrae control the motor activities and senses of the trunk. If a damage occurs in this area, an imbalance occurs in the breathing, cardiac rhythm or related organs, it also causes a discomfort in the organs located in the trunk, abdomen, and affects the genital and sexual abilities.
Lumbar Vertebrae:
The 5 vertebrae that follow the thoracic vertebra and locate in the lumbar region are called the lumbar vertebrae. If a mild damage to the lumbar vertebrae compresses the spinal cord, a pain and numbness will occur, and if the damage is severe, a paraplegic paralysis will occur; no control over the legs and lower functions including the genital and sexual abilities.
Sacral Vertebrae:
The 5 vertebrae located in the coccyx region are called sacral vertebrae. These vertebrae control the feet (below the knee) and sexual-genital functions. As a result of damage to this area, the sensory and motor activities in feet and genital-sexual functions will be lost.
Coccygeal Vertebrae:
The 3-4 vertebrae located at the tip of the coccyx, merged together and stunted are called coccygeal vertebrae. These vertebrae do not control a single area, and the traumas to be experienced here do not cause a significant paralysis, but there may occur dysfunctions only in the feet.
When classified in this way, the inner drum-shaped oval parts of the vertebrae are called the corpus, the protrusions on the right and left sides are called the protrusion, the posterior horn-shaped extension is called the spinous protrusion.Vertebrae are connected to each other with cushions called the discus located between vertebrae.
The role of the discs in the spinal system prevents the bones from abrasion by touching each other and provides flexibility that allows the spine to move.
The spine is also tightly enveloped by the connective tissues called ligaments that surround it on all sides. The ligaments that hold the anterior region are called the anterior ligament, and those that hold the posterior region are called the posterior ligament.
The spinal system, which forms an integrity with all these elements, performs its function in a stable (ie. fixed) state and protects the spinal cord. As mentioned at the beginning, the Spinal Cord is located inside the spine. However, the spinal cord in this canal is located inside the CSF, that is, the cerebrospinal fluid, which is surrounded by a membrane called dura. CS Facts as a hydraulic buffer that prevents the spinal cord from touching to the dura and bone.
The spinal cord is anatomically composed of two parts. The first partis the main part extending from C1 to L1-2. The second part is the part called the cauda equina, which consists of a bundle of nerve fibers that extend down from this area and appear as a horse's tail. Anatomically structured in this way, the spinal cord establishes the connection with the organs through the nerve roots which are extended between the vertebrae.
The distribution of 31 pairs of nerve roots according to the regions is as follows:
- Cervical Region 7+1=8 pairs.
- ThoracalRegion12 pairs.
- LumbarRegion5 pairs.
- SacralRegion5 pairs.
- CoccygealRegion1 pair.
The spinal cord, with these anatomical features, can lose its function if it is compressed due to a disease or trauma. Although the disease or trauma that causes a compression can affect the spinal cord directly, this situation is mostly due to a disease or trauma that develops in the spine, i.e., the vertebrae bones. The bone fragments broken fromthe vertebrae, especially as a result of an accident, can damage the spinal cord passing through the vertebra (creating an incision), causing a spinal cord paralysis.
