We Are Always Here for Your Health.
A Healthy life is everyone's right!
FILL IN THE FORM TO GET QUOTE
Radiology
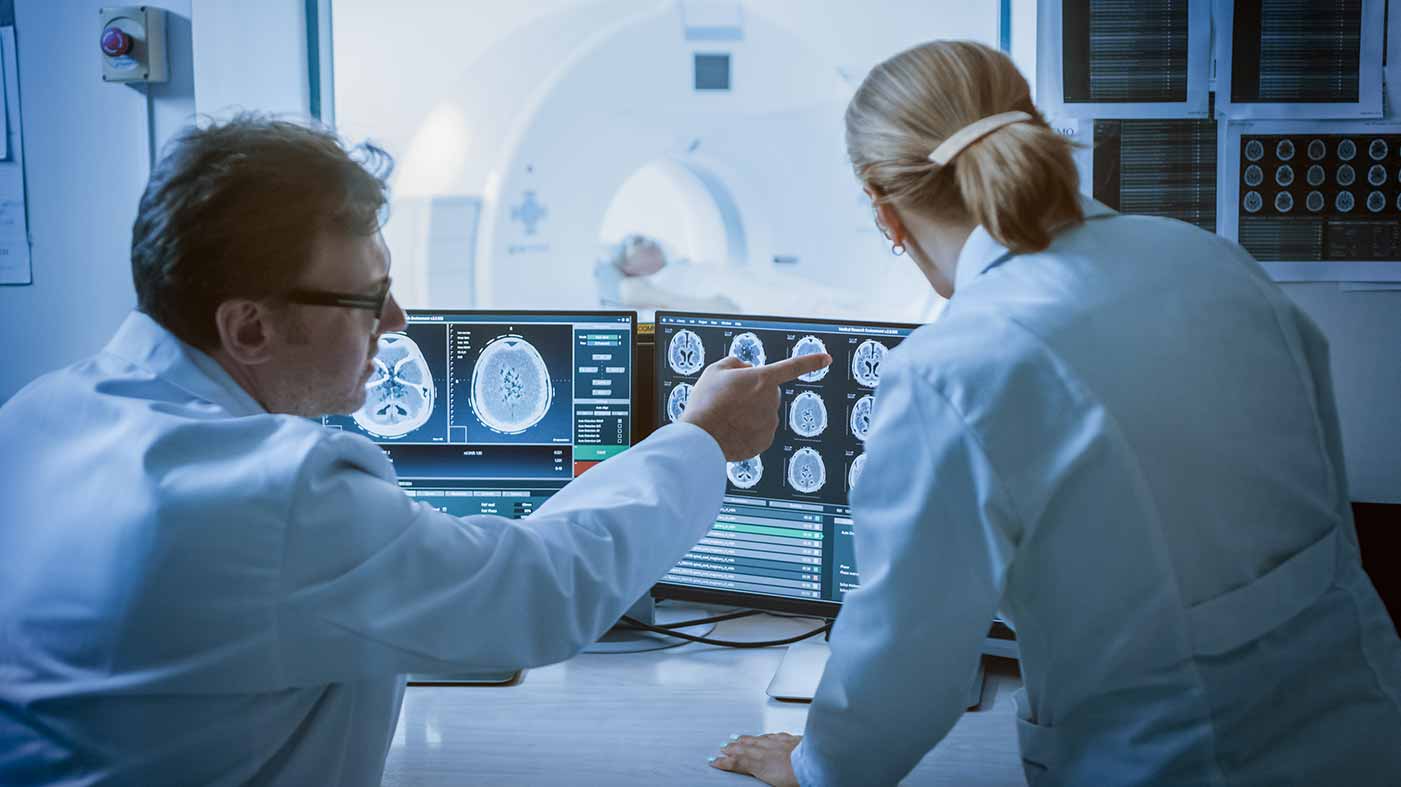
The Radiology is a branch of medicine that uses various imaging technologies in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Radiological examinations are performed in almost every field of the health sector. Radiology uses different imaging methods including x-ray, magnetic resonance (MR), computerized tomography (CT), and PET scanning to produce images of intra-body structures. It is divided into two broad areas as the diagnostic radiology and the interventional radiology. Radiology is a vital component of most medical decisions affecting the patients, and the radiologists can cooperate with all clinical specialties.
The diagnostic radiologist is the last link in the diagnostic chain, examining the images that can help to evaluate and support the diagnosis. A medical imaging specialist, who can use and manage the technical equipment to produce images, is called a radiological technologist. Although the unit where the radiological examinations are performed in hospitals is usually called the Radiology, it can also be called x-ray or imaging unit.
What diseases does the Radiology deal with?
Radiologists can cooperate with all medical physicians depending on the patient's condition. The main focus of the diagnostic radiography is diagnosis and monitoring of the diseases, skeletal and soft tissue abnormalities, and trauma. Radiology is necessary in the diagnosis of many diseases, especially cancer. (2) Also:
- In the diagnosis of bone and lung diseases
- For examining foreign objects
- For injuries and in the emergency medicine
- For breast diseases
- In the diagnosis of osteoporosis
- In the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases
- In the diagnosis of diseases of intra corporeal organs
- In the follow-up of pregnancy
- In the diagnosis of muscular-ligament structure and skeletal system disorders
- In the follow-up of the nervous system including the spine, spinal cord, brain, head, neck, waist, and for neuroradiology
- In imaging of the stomach, abdomen, breast, soft tissue lesions
- In the examination of gynecological and pediatric diseases
The nuclear medicine applications including the tests of bone scan, thyroid scan and thallium cardiac stress test are also included in the field of Radiology.
The pandemics can be detected more quickly and accurately owing to the technological developments that enable the electronic storage of radiological images.
The Diagnostic Radiology
To diagnose the cause of the symptoms
To check how well the body responds to the treatment received.
It can be used for early diagnosis of different diseases such as breast cancer, colon cancer or cardiac disease.
In the diagnostic radiology, intra corporeal structures are screened and the diagnostic radiologists interpret these images.
The most commonly used diagnostic radiological tests:
- Computerized tomography (CT) including CT angiography.
- Fluoroscopy including upper GI (gastrointestinal tract) and barium enemas
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- Mammography
- Nuclear medicine tests, including the bone scan, thyroid scan, and thallium cardiac stress test
- Plain x-ray with chest x-ray
- Positron emission tomography, called PET imaging or PET scan
- Ultrasound
Interventional radiology
The interventional radiology provides an imaging guidance for minimally invasive procedures in the treatment of patients not undergoing an open surgery. Imaging methods including CT, ultrasonography, MRI, and fluoroscopy are radiological techniques used to guide the medical procedures.
Examples of interventional radiology procedures:
- Angiography (vessel imaging) or angioplasty (vasodilation) and stent placement.
- Embolization to control the bleeding.
- Cancer therapies: Tumor embolization by chemoembolization (embolization with microspheres loaded with the chemotherapy drugs) or Y-90 radioembolization (Yitrium-90 microsphere)
- Tumor ablation therapies: Radiofrequency ablation (heat evaporation), cryoablation (freezing the tumor) or microwave ablation (heat evaporation)
- Spine and backbone fracture treatments: Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
- Fine needle biopsies: lungs, thyroid gland or other organs
- Breast biopsy: Stereotactic or ultrasound techniques
- Treatment of occlusion in the uterine artery: Uterine artery embolization
- Insertionof a feeding tube.
- Placement of venous access catheters such as ports and PICC (Peak catheter).
Diagnostic tools used by radiology
X-rays:
Radiographs created by using X-rays are used to examine the bones, chest and abdomen, and foreign objects. Fluoroscopy can be performed to monitorize a moving image of the digestive system. It can be used in combination with a contrast agent to create an angiography that shows the blood vessels.
Computerized tomography (CT)
CT creates the cross-sectional images of the body by using multiple X-rays sent from the CT machine to the area to be imaged. It is called "computerized tomography" because it produces an image based on the computer calculations. It can examine the functions of the body and organs. It uses the radioactive tracers that travel inside the body while creating the image.
Magnetic Resonance (MR)
MR creates high-quality images of the body structures with the help of a computer program by usinga magnetic field and the radio waves. This technique, which creates the images by using the potential energy stored in the hydrogen atoms of the body, is called Magnetic Resonance Imaging. It does not need any radiation.
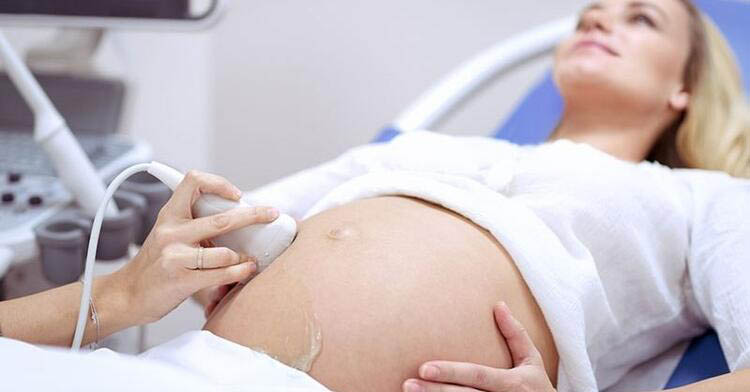
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography uses the sound waves to create moving images on a monitor. It is the cheapest and harmless imaging technique. Ultrasound probes (transducers) use the acoustic energy above the hearing threshold in humans to produce the images. Since an ionizing radiation is not used in ultrasonography, it is especially preferred for imaging the children and pregnant women.
Mammography
Mammogram is a specially reinforced and positioned X-ray imaging for the breast tissues. Mammography is the most ideal test for an early diagnosis of the breast cancer.
Fluoroscopy
It is a technique of producing the real-time images and moving images of the body with the help of X-rays for procedures such as stent placement for narrowed vessels and drainage catheters or imaging the gastrointestinal tract. The radiation dose used is higher than the conventional radiography.
Nuclear Medicine
To create the nuclear medicine images, a short-lived radioactive agent is injected to the patient, and then the radiation emitted from the patient is recorded and processed on the computer.
